
What is an IP Address?
IP Address = ( Internet Protocol Address )
computer must have an address so that other computers can find and locate mine in order to deliver that particular file or webpage that I am requesting. In technical terms, that address is called IP Address or Internet Protocol Address.
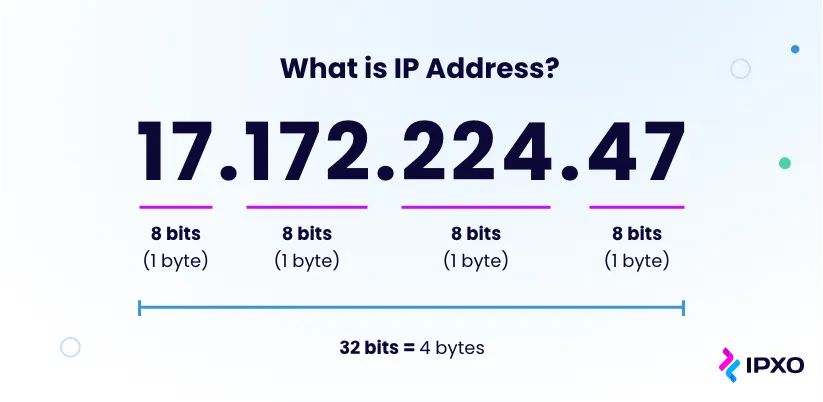
IP address is a unique address that is used to identify computers or nodes on the internet. This address is just a string of numbers written in a certain format. It is generally expressed in a set of numbers for example 192.155.12.1.
Here each number in the set is from 0 to 255 range. Or we can say that a full IP address ranges from 0.0.0.0. to 255.255.255.255.
What is an IP Address?
IP Address = ( Internet Protocol Address )
computer must have an address so that other computers can find and locate mine in order to deliver that particular file or webpage that I am requesting. In technical terms, that address is called IP Address or Internet Protocol Address.
IP address is a unique address that is used to identify computers or nodes on the internet. This address is just a string of numbers written in a certain format. It is generally expressed in a set of numbers for example 192.155.12.1.
Here each number in the set is from 0 to 255 range. Or we can say that a full IP address ranges from 0.0.0.0. to 255.255.255.255.
And these IP addresses are assigned by IANA
( Internet Corporation For Internet Assigned Numbers Authority ).

How do IP addresses really work?
* Your device directly requests your Internet Service Provider which then grants your device access to the web.
* And an IP Address is assigned to your device from the given range available.
* Your internet activity goes through your service provider, and they route it back to you, using your IP address.
* Your IP address can change. For example, turning your router on or off can change your IP Address.
* When you are out from your home location your ho me IP address doesn’t accompany you. It changes as you change the network of your device.
Information transmitted over the internet is sent in discrete blocks, called packets, which contain the data a recipient requests and a sender wants to communicate.
If you think of these packets as physical parcels, an IP address is like the postal address a sender uses to make sure the parcel gets to the right recipient.
The process of being assigned and using an IP address generally looks like this:

IP address types
Types of IP addresses you’ll hear referred to include:
Static
Dynamic
Public
Private
Dedicated
Shared
IPv4
IPv6
These types fall into separate sub-categories, each representing a different feature or function of IP addresses.